RBI moves to wind up CDR system
Nearly 1.32 trillion of bad loans are presently undergoing restructuring in the CDR cell
 Premium
Premium
Mumbai: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is moving to shut down the corporate debt restructuring (CDR) system, its very first loan recast mechanism, following its latest framework on stressed asset resolution, three people familiar with the matter said. The regulator has directed the CDR cell to transfer all pending cases to respective lead banks to complete the resolution process, the people cited above said on condition of anonymity.
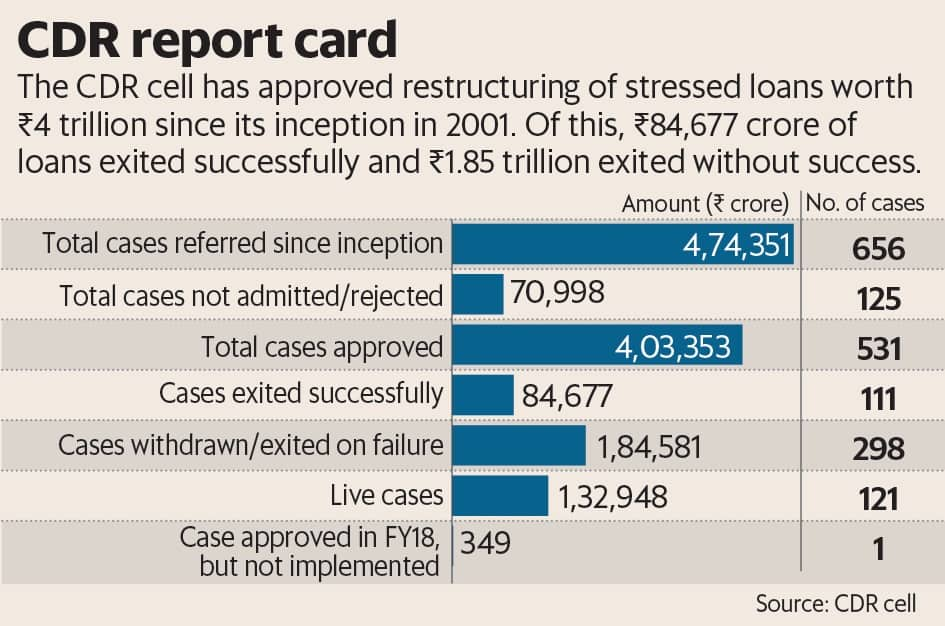
According to the latest available data, the CDR cell has approved restructuring of stressed loans worth ₹ 4 trillion since its inception in 2001. Of this, ₹ 84,677 crore worth of loans exited the CDR cell successfully and ₹ 1.84 trillion exited without success. Nearly ₹ 1.32 trillion worth of bad loans are presently undergoing restructuring in the cell.
RBI’s decision to wind up the cell comes after it issued a circular on 12 February withdrawing all existing restructuring schemes. This included the CDR scheme, strategic debt restructuring (SDR) scheme and scheme for sustainable structuring of stressed assets (S4A) and 5/25. The central bank has asked all banks to initiate resolution plans as soon as a corporate default happens, and refer it for bankruptcy proceedings in the event of a failure in restructuring.
The CDR system was framed 17 years ago to restructure corporate debt outside the purview of debt recovery tribunals (DRT) and the Board for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction. Its three-tiered structure consisted of CDR Standing Forum, CDR Empowered Group and CDR Cell. The Standing Forum was responsible for laying down all policies and guidelines related to debt restructuring, while the CDR cell was responsible for scrutinising all restructuring proposals from borrowers and lenders. The final decision on approving the restructuring package was taken by the CDR Empowered Group.
Under the CDR cell rules, at least 75% of creditors (by value) should approve the resolution plan, which would make it binding on the remaining 25%.
The reason for CDR’s failure can be attributed to the inability of promoters to infuse equity capital and non-compliance with the CDR agreement in pledging shares in favour of lenders’ consortia. The cell also prescribed a shorter interest payment moratorium of two years for all types of loans including infrastructure projects, which typically take a long time to develop and pay back.
According to Siby Antony, chairman of Edelweiss Asset Reconstruction Co., CDR was one of the best restructuring schemes introduced by RBI. Antony was previously the executive director of IDBI Bank, and was responsible for setting up the CDR cell. “The success rate of CDR during the initial period up to 2009 was more than 90%. In fact, gross NPA of the banking system during this period which was as high as 15%, came down to less than 2%. But the problem started post Lehman crisis and the global meltdown, when stress began to build up in the system. At the same time, CDR went through regulatory changes which required that net present value of a loan after restructuring should be retained. This led to ballooning of debt which ultimately led to the collapse of the CDR framework," said Antony.
Unlock a world of Benefits! From insightful newsletters to real-time stock tracking, breaking news and a personalized newsfeed – it's all here, just a click away! Login Now!